What is Hydrogen Car and How They Work?
As the world faces an ever-growing challenge in combating climate change and reducing carbon emissions, the need for sustainable transportation has never been more critical. One promising technology that has captured the imagination of scientists, engineers, and environmentalists alike is the hydrogen car. Often touted as the vehicle of the future, the hydrogen car holds the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry and contribute significantly to a cleaner and greener world.
What is Hydrogen Fuel Cell Car and How They Work
What is a Hydrogen Car?
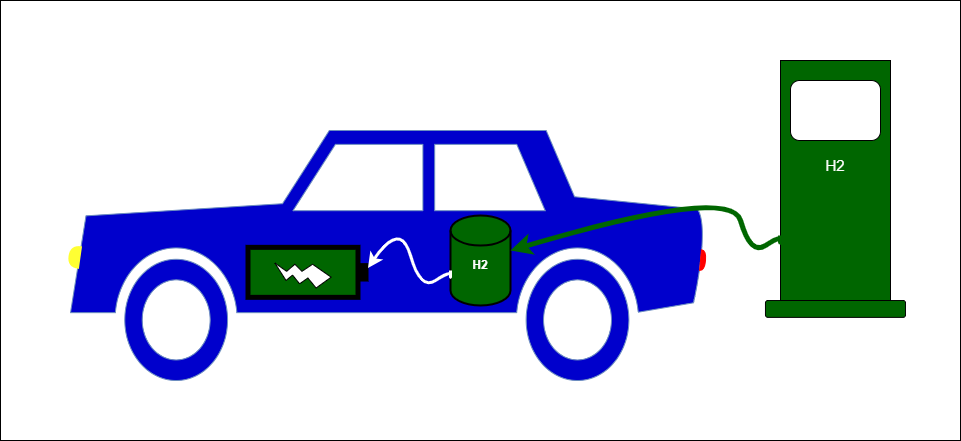
A hydrogen car, also known as a fuel cell vehicle (FCV), is an automobile that uses hydrogen gas to generate electricity, powering an electric motor that propels the vehicle. The core of the hydrogen car is its fuel cell, which converts the chemical energy stored in hydrogen into electrical energy through a chemical reaction with oxygen from the air. The only byproduct of this reaction is water vapor, making hydrogen cars emission-free during operation.
How Does a Hydrogen Car Work?
The primary components of a hydrogen car include:
- Hydrogen Storage: Hydrogen gas is stored in high-pressure tanks or cryogenic tanks, ensuring it remains in a compact state, making it suitable for automotive applications.
- Fuel Cell Stack: The heart of the hydrogen car is the fuel cell stack, where the actual conversion of hydrogen into electricity takes place. The stack consists of individual fuel cells, each containing a positive electrode (the anode) and a negative electrode (the cathode) separated by an electrolyte.
- Electric Motor: The electricity produced by the fuel cell stack is used to power an electric motor that drives the vehicle's wheels, providing propulsion.
- Battery: In some designs, hydrogen cars also have a small battery pack to store excess electricity generated during high-demand situations or regenerative braking, helping provide an extra power boost when needed.
Advantages of Hydrogen Cars:
- Zero Emissions: The most significant advantage of hydrogen cars is that they emit only water vapor during operation. This makes them a promising solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
- Fast Refueling: Hydrogen refueling takes a similar amount of time to conventional gasoline refueling, typically around 3 to 5 minutes. This fast refueling time eliminates the range anxiety often associated with battery electric vehicles (BEVs) that require longer charging times.
- Long Driving Range: Hydrogen cars can achieve longer driving ranges compared to most battery electric vehicles. This is particularly advantageous for large vehicles and long-haul transportation, making hydrogen an attractive option for heavy-duty applications.
Challenges and Hurdles:
Despite its immense potential, the widespread adoption of hydrogen cars faces several challenges:
- Infrastructure: One of the most significant hurdles is the lack of a widespread hydrogen refueling infrastructure. Building a comprehensive network of hydrogen stations requires significant investments and collaboration between governments, private industries, and other stakeholders.
- Storage and Safety: Storing hydrogen safely in vehicles is a challenge. Although significant advancements have been made in hydrogen tank technology, ensuring the safe containment of hydrogen is essential for public acceptance.



